Introduction
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is one of the most powerful project scheduling techniques used in the construction industry. From high-rise buildings and highways to industrial plants and infrastructure projects, CPM provides a structured, logical, and data-driven way to plan, monitor, and control project schedules. In modern construction environments where delays translate directly into cost overruns, penalties, and reputational damage, CPM is no longer optional—it is a core project management competency.

In real construction projects, delays are rarely caused by a single issue. They are usually the result of interconnected activities, such as late material delivery, design changes, labor shortages, or inspection delays. CPM helps project teams understand which activities directly control project completion time and which ones have flexibility. This allows managers to prioritize resources, focus on critical tasks, and make informed decisions under pressure.
In simple terms, CPM answers three fundamental questions:
- What activities must be completed?
- In what sequence must they occur?
- Which activities cannot be delayed without delaying the project?
For construction professionals, CPM is not just a planning tool—it is a risk management system, decision-making framework, and control mechanism. When used correctly, it improves schedule reliability, reduces claims, minimizes disputes, and strengthens client trust.
This complete walkthrough explains CPM from fundamentals to advanced applications, with worked examples, formulas, real-world construction case studies, practical checklists, tools, and common mistakes—designed specifically for engineers, project managers, planners, and construction professionals.
Table of Contents
Why CPM Matters in Construction
Schedule Control
Construction projects operate under tight deadlines. CPM identifies time-critical activities so teams focus on tasks that directly affect completion.
Cost Control
Delays increase costs through:
- Extended site overheads
- Equipment rentals
- Labor idle time
- Liquidated damages
Studies show that schedule overruns increase total project costs by 8–15% on average in large construction projects .
Risk Management
CPM helps predict schedule risks early and supports proactive mitigation planning.
Contractual & Legal Importance
CPM schedules are widely accepted in claims, arbitration, and dispute resolution as evidence-based planning tools.
Fundamental Concepts of CPM
Key Terms
- Activity: A task with duration (e.g., foundation excavation)
- Node/Event: Start or end point of activities
- Critical Path: Longest duration path through the network
- Float/Slack: Allowable delay without affecting project completion
CPM Formula (Core Concept)
Project Duration:
T=max(∑di)
Where:
- di = duration of activities in each path
- The longest path = critical path
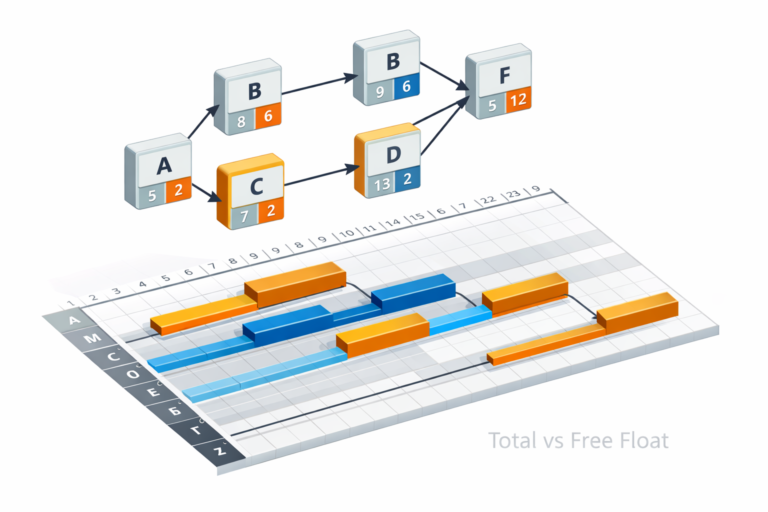
Types of Float
- Total Float (TF): TF=LS−ES=LF−EF
- Free Float (FF): Delay allowed without affecting successors
CPM Methodology Step-by-Step
Step 1: Activity Identification
Checklist:
- Break project into work packages
- Use WBS
- Define measurable tasks
Step 2: Sequencing
- Finish-to-Start
- Start-to-Start
- Finish-to-Finish
Step 3: Duration Estimation
Use:
- Historical data
- Productivity rates
- Site constraints
Step 4: Network Diagram Development
Create logical flow of activities.
Step 5: Critical Path Calculation
Forward pass + backward pass.
Worked Example 1 (With Calculations)
| Activity | Duration (Days) | Predecessor |
|---|---|---|
| A | 5 | – |
| B | 4 | A |
| C | 6 | A |
| D | 3 | B, C |
Paths:
- A-B-D = 5+4+3 = 12 days
- A-C-D = 5+6+3 = 14 days → Critical Path
Project Duration = 14 days
Tools & Software for CPM
| Tool | Use Case | Industry Use |
| Primavera P6 | Large infrastructure | High |
| MS Project | Medium projects | High |
| Asta Powerproject | Construction | Medium |
| TILOS | Linear projects | Specialized |
Common Mistakes & Solutions
- Overloaded critical path → Use resource leveling
- Wrong dependencies → Validate logic with site engineers
- Unrealistic durations → Use historical data
- Ignoring float → Track non-critical activities
- Static schedules → Update weekly
Case Study 1: Residential Building Project
A 12-floor residential building used CPM scheduling.
Results:
- Planned duration: 420 days
- Actual completion: 402 days
- Savings: 18 days
- Cost saving: ~6% overhead reduction
Case Study 2: Highway Flyover Project
CPM enabled parallel execution of:
- Pier construction
- Girder casting
- Utility shifting
Outcome:
- Delay risk reduced by 22%
Case Study 3: Industrial Plant Expansion
Using CPM and resource leveling:
- Equipment utilization improved by 18%
- Idle labor reduced by 25%
FAQ
Q1: What is the Critical Path Method in construction?
CPM is a scheduling technique that identifies activities that directly control project duration.
Q2: Why is CPM better than bar charts?
It shows logic, dependencies, and risks.
Q3: Can CPM handle delays?
Yes, through float analysis and re-baselining.
Q4: Is CPM legally accepted?
Yes, widely used in claims.
Q5: Which software is best for CPM?
Primavera P6 and MS Project.
Q6: Can small projects use CPM?
Yes, even housing projects benefit.
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is the backbone of modern construction project scheduling. It transforms complex projects into structured, logical networks that teams can manage, control, and optimize. By identifying time-critical activities, CPM allows project managers to allocate resources strategically, reduce delays, manage risks, and protect profitability.
Construction projects today face increasing complexity, tighter timelines, higher client expectations, and stricter contractual obligations. CPM provides a scientific, proven, and industry-accepted framework to manage these pressures. When integrated with digital tools, BIM, and real-time monitoring systems, CPM becomes a powerful decision-support engine rather than just a planning tool.
For engineers, planners, and construction managers, mastering CPM is not just a technical skill—it is a career advantage. Projects delivered on time build trust, reputation, and long-term business growth.
The most successful construction organizations treat CPM not as paperwork, but as a living management system that evolves with the project.
Free Resources
Access free CPM templates, planning sheets, and construction scheduling guides from Famcod to implement CPM on live projects.
Related Articles
- Critical Path Method (CPM) Guide for Construction 2026
- Dependency Types in Construction Scheduling (FS, SS, FF, SF) Explained: Complete Guide 2026
- Float Calculation Methods: Total Float vs Free Float in Construction Scheduling
- Schedule Compression Techniques in Construction: Crashing vs Fast-Tracking Explained
- Resource Allocation Strategies in Planning for Construction Projects
Recommended Resources
“Construction Project Management” – Comprehensive CPM fundamentals.
[Amazon Affiliate Link]
“Project Scheduling and Cost Control” – Practical planning techniques.
[Amazon Affiliate Link]
“Critical Path Method in Construction” – CPM-focused guide.
[Amazon Affiliate Link]
Coursera: “Construction Scheduling”
[Coursera Affiliate Link]
Coursera: “Project Management Principles”
[Coursera Affiliate Link]